Read Blog 
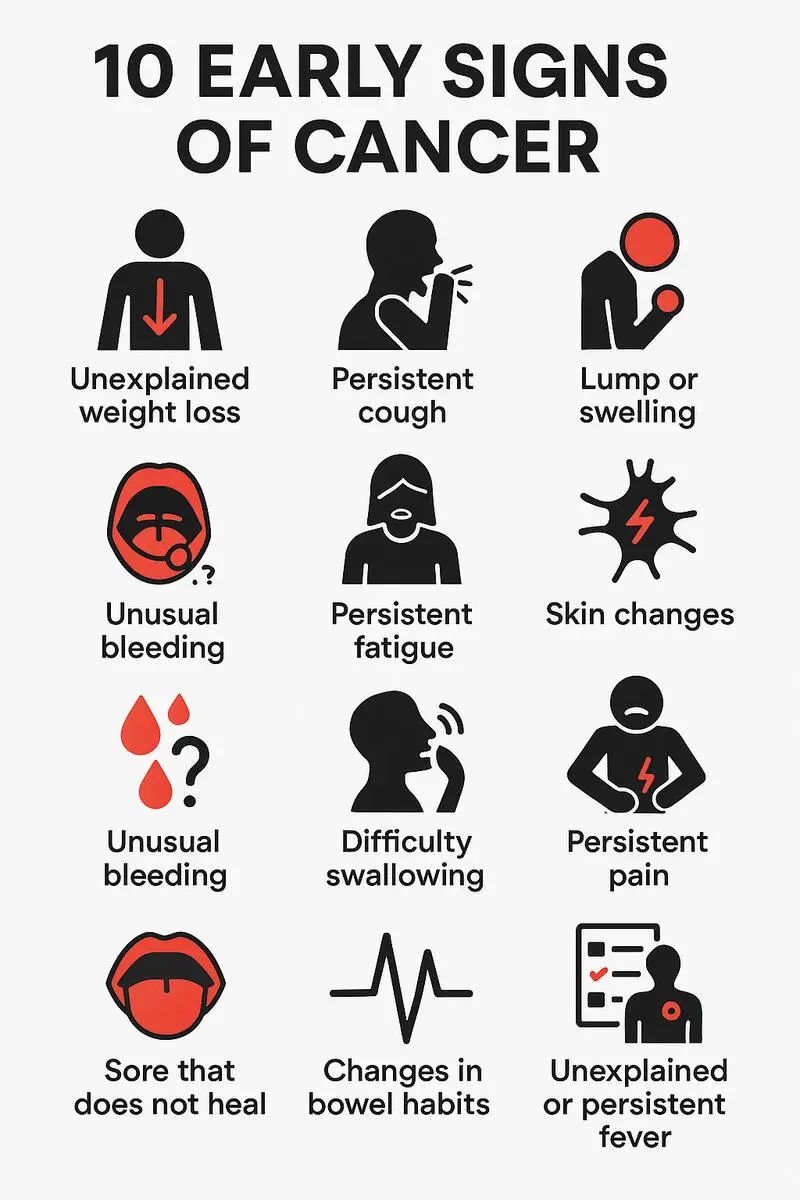
10 Early Signs of Cancer Most Indians Ignore
Cancer is a growing concern in India, with cases rising due to lifestyle changes, genetic factors, and environmental triggers. Early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment and recovery. Unfortunately, many people tend to overlook early signs of cancer, mistaking them for minor health issues. In this article, we will discuss 10 early signs of cancer that most Indians ignore, how to detect them early, and essential cancer prevention tips.
1. Unexplained Weight Loss
If you are losing weight without any changes in diet or exercise, it could be a warning sign of cancer. Cancers of the stomach, pancreas, esophagus, and lungs can cause sudden weight loss. If you experience unexplained weight loss of more than 5 kg, consult a doctor immediately.
2. Persistent Fatigue
Feeling excessively tired despite getting enough rest may indicate an underlying health issue, including cancer. Leukemia, colon, and stomach cancers are often linked to extreme fatigue. If fatigue persists without an identifiable reason, it is advisable to get a medical evaluation.
3. Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits
Frequent diarrhea, constipation, or blood in the stool may signal colorectal cancer, while changes in urination patterns may indicate bladder or prostate cancer. If you notice prolonged changes in your bowel or bladder habits, seek medical attention.
4. Non-Healing Sores
A sore that does not heal within a few weeks could be a sign of oral cancer or skin cancer. Smokers and tobacco users should be especially vigilant about mouth ulcers, as they are at higher risk of developing signs of oral cancer.
5. Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
A cough lasting more than three weeks, especially if accompanied by blood, could be a symptom of lung cancer. Hoarseness that persists might be linked to throat or thyroid cancer. How to detect cancer early in such cases involves consulting a specialist if respiratory symptoms do not improve.
6. Lumps or Thickening of Tissue
The presence of lumps in the breast, testicles, or other parts of the body should not be ignored. Common cancer types in India, such as breast and testicular cancer, often present as painless lumps in their early stages. Early medical evaluation can prevent progression.
7. Difficulty Swallowing
Persistent difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, could be an early symptom of throat, esophageal, or stomach cancer. If swallowing problems continue despite dietary adjustments, a medical examination is necessary.
8. Unexplained Bleeding
Unusual bleeding, such as blood in urine, stool, or coughing up blood, is a serious warning sign of cancer. Cervical and endometrial cancers may cause abnormal vaginal bleeding. It is crucial to get tested if such symptoms occur.
9. Skin Changes
Skin abnormalities, such as dark patches, changes in moles, or persistent itching, can be indicators of skin cancer. If a mole grows, changes color, or starts bleeding, it is important to consult a dermatologist immediately.
10. Persistent Pain
Pain that does not go away, especially in the bones or back, can sometimes be an early sign of cancer. While pain alone is not definitive, unexplained or long-lasting pain should be evaluated by a medical professional.
How to Detect Cancer Early
Early detection greatly improves the chances of successful treatment. Here are some tips to catch cancer in its initial stages:
-
Regular Health Check-ups: Routine screenings, such as mammograms, Pap smears, and colonoscopies, help in detecting cancer before symptoms appear.
-
Self-Examinations: Checking for lumps, unusual moles, or changes in bodily functions can help identify potential issues early.
-
Knowing Family History: If there is a family history of cancer, it is advisable to go for genetic counseling and regular screenings.
-
Seeking Medical Attention Promptly: Do not ignore persistent symptoms. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment.
Cancer Prevention Tips
While cancer cannot always be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk. Here are some essential cancer prevention tips:
-
Quit Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco consumption is one of the leading causes of signs of oral cancer and lung cancer in India. Avoiding tobacco can drastically reduce your risk.
-
Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and lowers cancer risk.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of several cancers, including breast and colorectal cancer. Regular exercise is key to maintaining a healthy weight.
-
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake has been linked to liver, breast, and digestive tract cancers. Limiting alcohol can help reduce cancer risk.
-
Protect Yourself from the Sun: Skin cancer can be prevented by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure.
-
Get Vaccinated: Vaccinations against Hepatitis B and HPV can prevent liver and cervical cancer, respectively.
-
Avoid Exposure to Carcinogens: Limit exposure to harmful chemicals, such as asbestos and radiation, that are known to cause cancer.
Conclusion
Awareness is the first step toward preventing and detecting cancer early. Ignoring early signs can lead to late-stage diagnosis and reduced treatment success. By understanding these early signs of cancer, following cancer prevention tips, and undergoing regular screenings, individuals can significantly lower their risk. If you experience any of these symptoms, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. How to detect cancer early is crucial knowledge that can save lives.
By staying informed and proactive, we can fight the rising incidence of common cancer types in India and ensure better health outcomes for all.