- Published on: Jul 27, 2021
- 3 minute read
- By: Cancer Expert
Easy Tips For Cancer Prevention
Hello everyone! Let's talk about keeping ourselves healthy and cancer prevention. It's like going on a journey to a better and brighter future. In a world where being healthy is like having a treasure, it's super important to know how to stop cancer from happening. Come along with us as we share easy tips and simple choices that can help you stay strong and avoid the risk of cancer.
What is Cancer and Can We Stop It?
Let's start with the basics. Cancer is a group of complicated diseases. It happens when our cells grow out of control and become abnormal. So, can we stop cancer from happening? Absolutely! Our journey begins by knowing the things that can increase the chance of getting cancer and taking steps to prevent it.
Know About Cancer Risks
Before we talk about stopping cancer, let's understand what might cause it. The common things that can make cancer more likely are our genes (which we can't change), getting older, things around us, and choices we make in how we live. Even though we can't change our genes or stop time, there are things we can do to lower our risk.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact
Now, let's chat about the choices we make every day – like what we eat, how we move, and the things we do regularly. These choices can either help protect us from getting sick, like cancer or make it more likely for us to get sick. One easy way to stay healthy is to eat a mix of good foods, like fruits, veggies, and whole grains, and try not to eat too much-processed food. It's a simple but powerful step to keep our bodies strong and prevent problems like cancer.
Moving Your Body to Stay Healthy
Moving your body is like putting on a superhero shield against cancer. When you do activities like walking, playing, or dancing regularly, it keeps your body in good shape and lowers the chance of getting different types of cancers. Let's look at why moving around is so important for cancer prevention and how it's a must for staying healthy.
Eat Right to Fight Cancer
Superfoods Against Cancer
Let's talk about how the food we eat can help us stay healthy and prevent cancer. Imagine your meals as a superhero team fighting against bad stuff in your body. Some superheroes in this team are veggies like broccoli and cauliflower, and fruits full of antioxidants, like berries. Learn tasty ways to add these superfoods to your meals every day.
Drink Water for a Healthy You
Now, let's talk about something super easy but so important – drinking water. It's like a magic potion for your health. Having enough water is not just good for your body, but it also helps lower the chance of getting certain types of cancers. Let's find out why drinking water is essential and how it makes your body not a nice place for cancer cells.
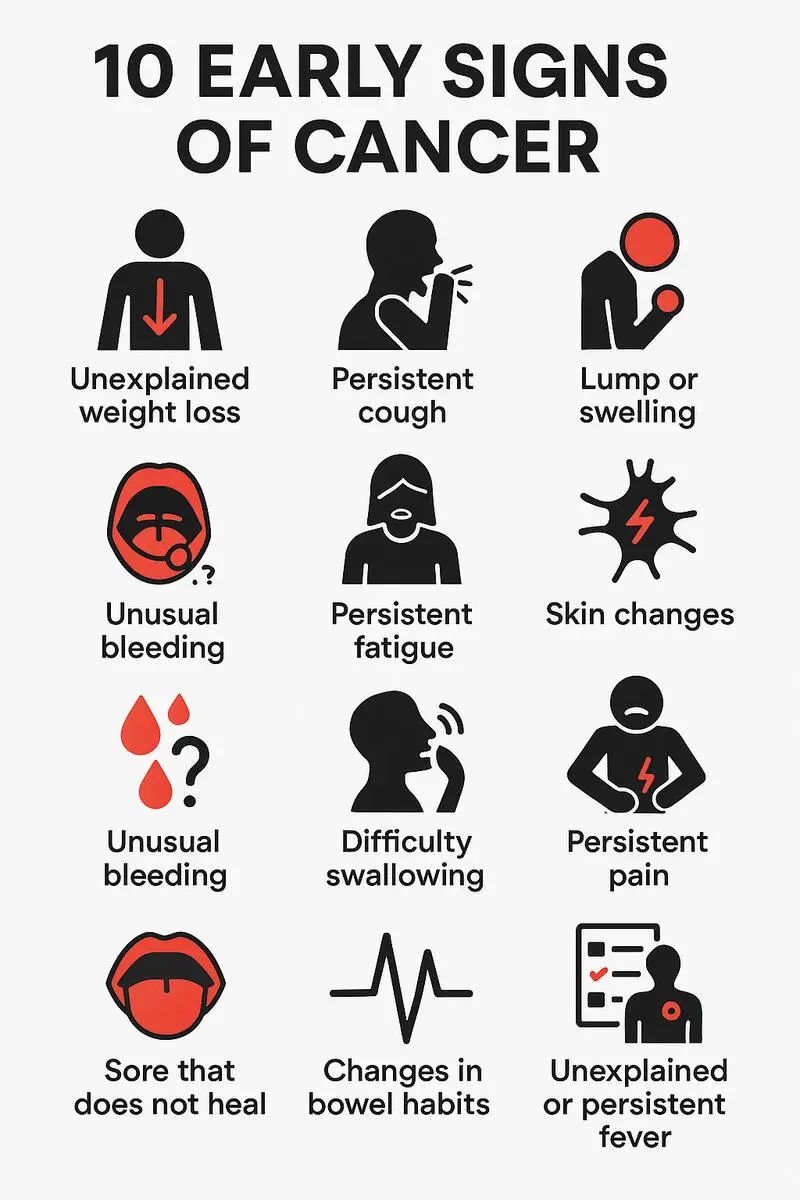
Checking for Cancer Early
We've talked a lot about stopping cancer from happening, but there's another important part: finding it early. Getting regular check-ups and knowing the signs that something might be wrong are like putting on armor to protect yourself from cancer. Let's learn about different ways to check for cancer and why it's super important to go to the doctor regularly to catch any problems early.
How Our Thoughts Affect Our Health
When we talk about staying healthy, it's not just about what we eat or how much we move. Our thoughts and feelings also play a big role. Feeling stressed or worried can make our bodies more likely to get sick, even with something as serious as cancer.
Here are some simple tips to help you feel better and keep your body strong:
1. Relax Your Mind: Take a few minutes each day to do something that helps you feel calm, like deep breathing or listening to music.
2. Think Positive: Try to focus on good things in your life. This can help your body stay healthy and ready to fight off illnesses.
3. Stay Happy: Doing things that make you happy, like spending time with friends or enjoying a hobby, can boost your immune system.
Remember, keeping your mind happy and stress-free is an important part of staying healthy and preventing diseases like cancer.
As we finish talking about cancer prevention, it's important to know that keeping ourselves healthy is something we can control. We can do this by knowing what might increase our chances of getting cancer, making good choices for how we live, and getting regular check up. By doing these things, we can make a future where we're not as scared of cancer. Think of this guide as your map, helping you live a strong and healthy life. Let's all be in charge of our health and create a world where preventing problems is not just an idea but a normal part of life.
Read FAQs
A. Yes, we can take steps to lower the chances of getting cancer. Eating healthy foods, staying active, and avoiding harmful things like tobacco are ways to help prevent cancer.
A. Reducing the risk of cancer involves making smart choices. Eat lots of fruits and veggies, exercise regularly, protect your skin from the sun, and stay away from tobacco and too much alcohol. These simple steps can lower the chances of getting cancer.
A. Cancer can be treated in various ways, like surgery, medicines (called chemotherapy), and radiation. Sometimes, to catch cancer early, doctors use screenings like mammograms or colonoscopies. Preventing cancer is also about knowing your body, going for regular check-ups, and avoiding things that can cause it, like smoking or excessive sun exposure.