- Published on: Apr 04, 2020
- 2 minute read
- By: Raj Dwivedi
Ways For Tackling Cancer Diagnoses, Misdiagnosis, And Treatment Delays
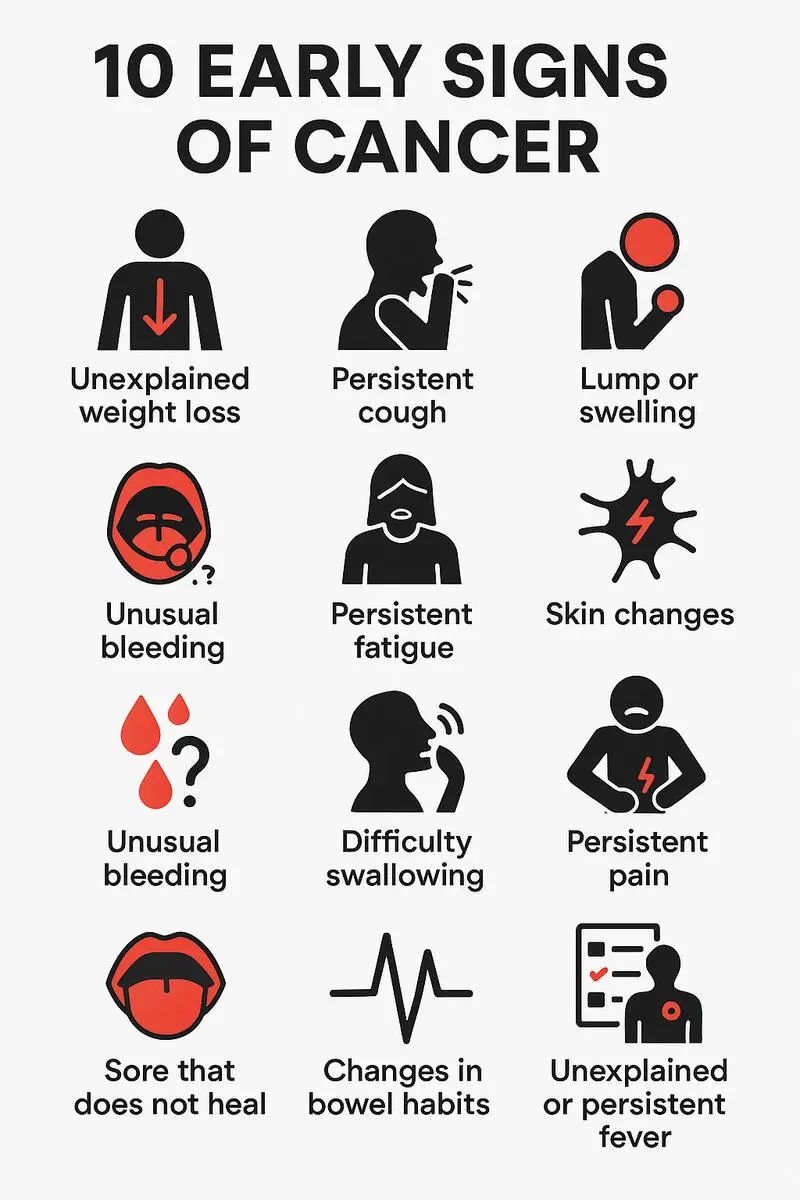
Have you ever found yourself caught in the delicate balance between life and uncertainty? The world of healthcare is rife with such moments, and when it comes to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, the stakes are higher than ever. How often does misdiagnosis or a delay in diagnosing cancer occur, and what are the implications? Are medical errors in cancer diagnosis more prevalent than we care to acknowledge? Let's embark on a journey to untangle the complexities surrounding misdiagnosed cancer, the importance of seeking a second opinion, and the potential pitfalls of delayed treatment.
Misdiagnosed Cancer: A Stark Reality
In the intricate tapestry of medical diagnoses, misdiagnosed cancer stands as a chilling reality. The consequences of misinterpreting symptoms, confusion in pathology reports, and various other factors can be profound. Let's delve into the shadows where misdiagnosed cancer lurks.
-
Misdiagnosed Cancer: A Silent Menace: The term "misdiagnosed cancer" carries a weight that sends shivers down the spine. From misinterpreted symptoms to confusion in pathology reports, various factors contribute to this unsettling reality.
-
Second Opinion for Cancer: A Ray of Hope When faced with a potentially life-altering diagnosis, seeking a second opinion becomes not just an option but a necessity. The journey toward accurate cancer diagnosis often involves multiple perspectives, each shedding light on different facets of the patient's condition.
Medical Errors in Cancer Diagnosis: Navigating the Perilous Path
The landscape of cancer diagnosis is fraught with challenges, and medical errors can become significant stumbling blocks. Let's explore the critical aspects of medical errors in cancer diagnosis:
-
Importance of Pathology in Cancer Diagnosis: The bedrock of accurate cancer diagnosis lies in pathology. An in-depth analysis of tissues and cells can be the difference between life-saving treatments and misplaced interventions.
-
X-ray Confusion: Untangling the Puzzle In the realm of cancer detection, X-rays play a pivotal role. However, confusion in interpreting these images can lead to misdiagnosis, setting the stage for a cascade of medical mistakes.
Treatment Delay: The Ticking Clock
As the clock ticks, every moment becomes critical in the battle against cancer. The repercussions of treatment delays are profound and often heart-wrenching. Let's understand the gravity of delayed treatment:
-
Medical Mistake: Unveiling the Culprit A crucial aspect of treatment delays lies in medical mistakes. Whether it's a misread diagnostic report or a delayed intervention, the consequences can be dire.
-
Delayed Treatment: A Race Against Time Time becomes an elusive ally in the face of delayed treatment. Cancer, when detected early, offers more treatment options and a higher chance of successful outcomes. Delaying the initiation of treatment can tip the scales unfavorably.
Online Doctor Consultation: Bridging the Gap
In our digital age, the advent of online doctor consultation has emerged as a powerful tool in the realm of healthcare. Let's explore how virtual consultations can bridge gaps and enhance the overall cancer diagnostic experience:
-
The Rise of Online Doctor Consultation : Technology has transcended traditional healthcare barriers, offering a lifeline to those seeking expert opinions from the comfort of their homes.
-
Navigating Uncertainties with Virtual Guidance: Online doctor consultation not only provides convenience but also serves as a valuable resource in navigating the uncertainties associated with cancer diagnosis.
1. Seek a Second Opinion: Empower yourself or your loved ones by actively seeking a second opinion when faced with a cancer diagnosis. Multiple perspectives can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the situation.
2. Emphasize the Importance of Pathology: Advocate for thorough pathology assessments. The accuracy of cancer diagnoses hinges on the meticulous examination of tissues and cells, ensuring a solid foundation for treatment decisions.
3. Explore Online Doctor Consultations: Leverage the convenience and accessibility of online doctor consultation. These virtual platforms can offer expert insights, especially in situations where geographical constraints might pose challenges.
In the journey through the intricacies of cancer diagnosis, let awareness be the guiding light, interest be the driving force, desire be the catalyst for change, and action be the beacon that leads to accurate diagnoses and timely treatments. After all, in the face of uncertainty, knowledge is the most potent weapon we possess.
Conclusion:
Taking Charge of the NarrativeIn the intricate dance between misdiagnosed cancer, medical errors, and treatment delays, one thing remains certain – the power of awareness and informed decision-making. As we navigate the complex terrain of cancer diagnosis, seeking a second opinion, understanding the nuances of pathology, and embracing the possibilities of online doctor consultations become crucial steps toward ensuring accurate and timely interventions.
Read FAQs
A. When diagnosed with cancer, avoid self-diagnosis through online searches, seek a second opinion for a comprehensive understanding, prioritize mental health to cope with the emotional impact, initiate treatment promptly to prevent disease progression, and foster a strong support system rather than isolating oneself.
A. Various treatments impede the growth of cancer cells, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, surgery, and angiogenesis inhibitors. These approaches aim to either directly destroy cancer cells or disrupt their ability to divide and form tumors.
A. The percentage of cancer patients refusing treatment varies, influenced by factors like cancer type and personal beliefs. Generally, a small percentage declines conventional treatments due to concerns about side effects, fear, or a preference for alternative therapies. Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for informed decision-making.
A. When diagnosed with cancer, avoid self-diagnosis through online searches, seek a second opinion for a comprehensive understanding, prioritize mental health to cope with the emotional impact, initiate treatment promptly to prevent disease progression, and foster a strong support system rather than isolating oneself.
A. The percentage of cancer patients refusing treatment varies, influenced by factors like cancer type and personal beliefs. Generally, a small percentage declines conventional treatments due to concerns about side effects, fear, or a preference for alternative therapies. Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for informed decision-making.