- Published on: Aug 09, 2024
- 2 minute read
- By: SecondMedic Expert
Understanding Mouth Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment Options
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, is a serious health condition that affects the tissues in your mouth. While it might seem scary, early detection and treatment can significantly improve your chances of recovery. In this blog, we will delve into the details of mouth cancer, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What is Mouth Cancer?
Mouth cancer is a broad term used for cancer that develops anywhere inside your mouth. This includes the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and roof or floor of your mouth. It's important to note that while anyone can develop mouth cancer, certain factors increase your risk.
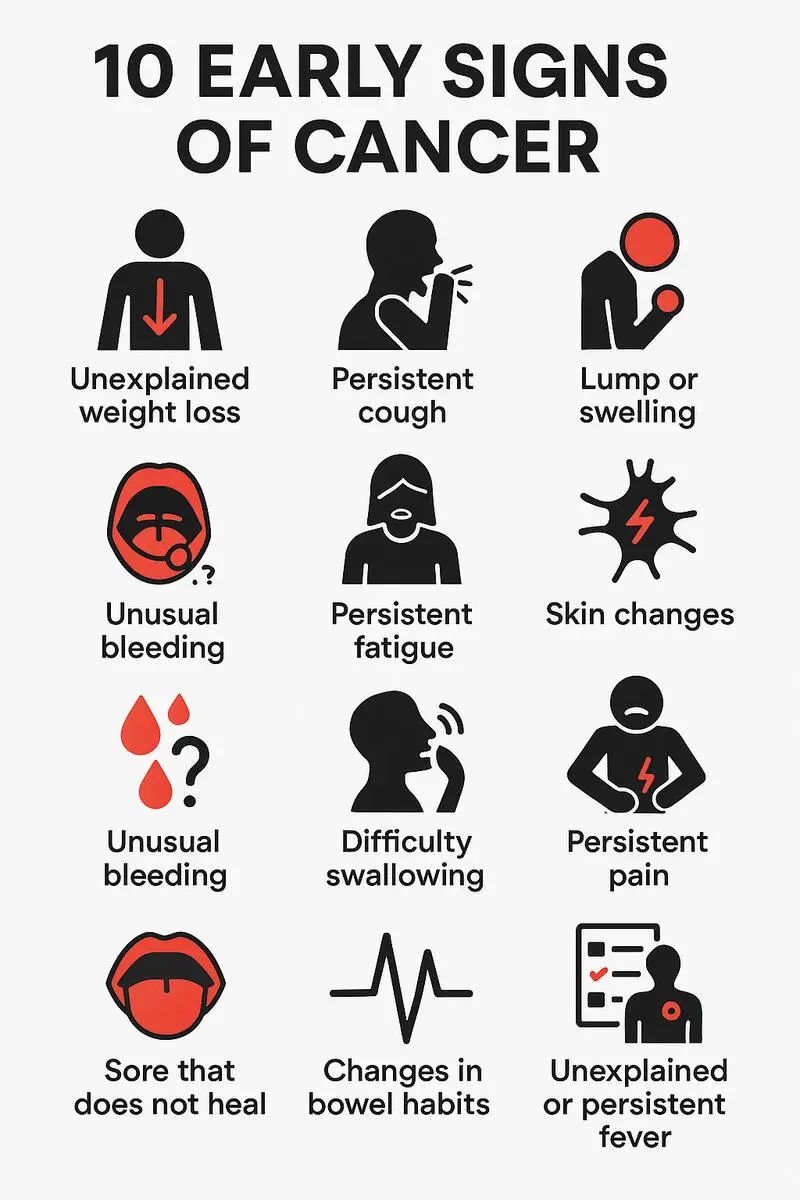
Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of mouth cancer is crucial for early detection. While these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if they persist.
Sores that don't heal: A persistent sore on your lip or inside your mouth that doesn't heal within two weeks is a common sign of mouth cancer.
White or red patches:These patches, often called leukoplakia or erythroplakia, can appear on the tongue, gums, or inner lining of your cheek.
Numbness: If you experience numbness in your lips, tongue, or other areas of your mouth, it could be a warning sign.
Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking: These issues can indicate an advanced stage of mouth cancer.
Loose teeth: Without an apparent reason, loose teeth might be a symptom.
Persistent sore throat or ear pain: These symptoms can also be associated with mouth cancer.
Causes of Mouth Cancer
Several factors contribute to the development of mouth cancer. Some of the primary causes include:
Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, and using smokeless tobacco products significantly increases your risk.
Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking, especially when combined with tobacco use, is a major risk factor.
Human papillomavirus (HPV): Certain types of HPV can contribute to the development of mouth and throat cancer.
Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting oral hygiene can create a breeding ground for bacteria and increase your risk.
Sun exposure: Excessive sun exposure can lead to lip cancer.
Weakened immune system: People with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to mouth cancer.
Risk Factors
In addition to the causes mentioned above, certain factors can increase your risk of developing mouth cancer:
Age: The risk increases with age.
Gender: Men are more likely to develop mouth cancer than women.
Diet: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables can contribute to the risk.
Chronic irritation or inflammation: Persistent irritation in the mouth can increase your risk.
Diagnosis
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, it's essential to consult a dentist or doctor for a proper diagnosis. They will conduct a thorough examination of your mouth, including your lips, tongue, gums, and throat. Additional tests, such as a biopsy, may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
The treatment for mouth cancer depends on several factors, including the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as your overall health. Common treatment options include:
Surgery:This involves removing the cancerous tissue and potentially lymph nodes.
Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to destroy cancer cells.
Targeted therapy: Uses drugs to attack specific cancer cells.
Prevention
While there's no guaranteed way to prevent mouth cancer, adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce your risk. Some preventive measures include:
Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products.
Limiting alcohol consumption.
Practicing good oral hygiene.
Protecting your lips from excessive sun exposure.
Regular dental check-ups.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Conclusion
Mouth cancer is a serious condition, but early detection and appropriate treatment offer a good chance of recovery. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors, you can take steps to protect your oral health. Remember, regular dental check-ups and prompt attention to any abnormalities in your mouth are crucial for early diagnosis and successful treatment.
Read FAQs
A. You know those annoying sores that just won’t heal? Or maybe you've noticed some weird white or red patches in your mouth? These could be signs of mouth cancer. Other things to watch for are numbness in your lips or tongue, trouble eating or talking, and loose teeth.
A. Smoking and drinking too much are big culprits. But did you know that the sun can hurt your lips too? Plus, if your immune system isn’t great, you might be more likely to get it. And don’t forget about that HPV thing – yeah, that can cause problems in your mouth too.
A. Treatment depends on how bad it is. Sometimes they need to do surgery to cut it out. Other times, radiation or chemo is the way to go. And there are newer treatments too, like targeted therapy.