- Published on: Aug 23, 2021
- 2 minute read
- By: SecondMedic Expert
Understanding Cancer Warning Signs
Have you ever wondered if your body is trying to tell you something important? Something that might seem insignificant but could be a warning sign of a much bigger issue. Well, what if I told you that your body might be giving you signals about a potential threat lurking within – cancer? Yes, it's a scary word, but it's essential to be aware of the warning signs. Let's delve into this vital topic together, exploring the different types of cancer, their causes, and most importantly, the red flags your body might be waving to get your attention.
Types of Cancer
Cancer isn't a one-size-fits-all disease. It comes in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics and challenges. Here are some common types
-
Blood Cancer: Also known as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma, blood cancer affects the production and function of your blood cells.
-
Skin Cancer: This type primarily manifests as unusual changes in your skin, including the development of moles or changes in existing ones.
-
Colon Cancer: Often silent in its early stages, colon cancer may exhibit symptoms such as changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, or abdominal discomfort.
Causes of Cancer
Understanding what causes cancer is like unraveling a mystery with multiple layers. While the exact causes may vary depending on the type of cancer, some common factors include:
-
Genetics: Certain genetic mutations can predispose individuals to cancer.
-
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can significantly increase your risk.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens such as asbestos, radon, and ultraviolet radiation can contribute to the development of cancer.
Reasons for Cancer
Why does cancer occur? It's a question that has puzzled scientists and researchers for decades. While there may not be a single definitive answer, here are some underlying reasons:
-
Cellular Abnormalities: Cancer often begins with mutations in the DNA of cells, causing them to grow and multiply uncontrollably.
-
Immune System Dysfunction: A weakened immune system may fail to recognize and destroy abnormal cells, allowing them to proliferate.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormone levels can influence cell growth and division, potentially leading to cancerous growth.
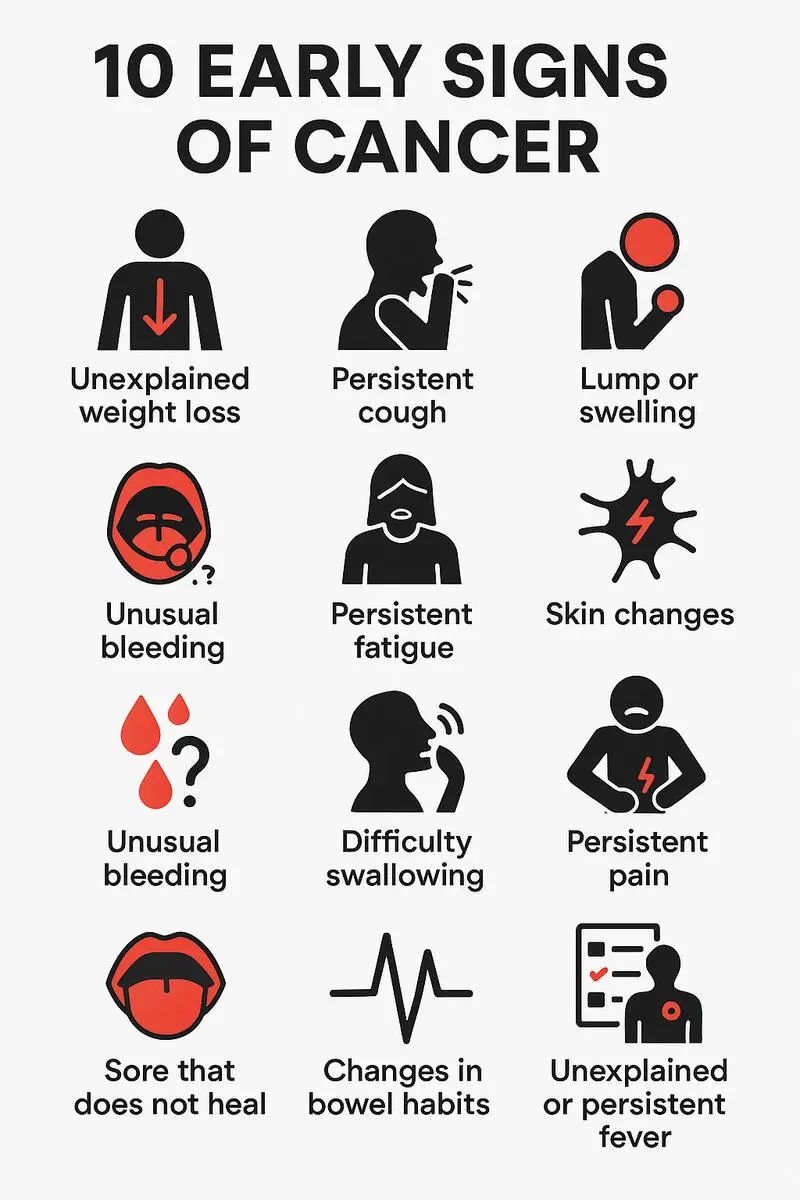
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Your body has a remarkable way of communicating with you, even when words fail. Paying attention to these subtle signals can help detect cancer in its early stages when treatment is most effective. Here are some warning signs to watch out for:
-
Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying could be a red flag for various types of cancer, including pancreatic, stomach, or lung cancer.
-
Persistent Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired despite adequate rest may indicate underlying health issues, including leukemia or colon cancer.
-
Changes in Skin Appearance: New moles, changes in the size or color of existing moles, or non-healing sores could signal the presence of skin cancer.
-
Digestive Troubles: Persistent indigestion, difficulty swallowing, or changes in bowel habits such as diarrhea or constipation may warrant further investigation for colon or stomach cancer.
-
Unexplained Pain: Chronic pain that doesn't resolve with typical treatments or is unrelated to any injury should be evaluated, as it could be a symptom of bone, brain, or ovarian cancer.
Online Doctor Consultation
In today's digital age, accessing medical advice and information has never been easier. If you notice any concerning symptoms or have questions about your health, don't hesitate to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional. Online doctor consultation offers a convenient and efficient way to address your concerns and receive personalized recommendations from the comfort of your own home.
Conclusion:
Cancer may be a formidable foe, but armed with knowledge and awareness, you can empower yourself to take proactive steps toward prevention and early detection. By familiarizing yourself with the warning signs, understanding the causes and risk factors, and prioritizing regular screenings and check-ups, you can stay one step ahead in the fight against cancer. Remember, your health is your most valuable asset – cherish it, nurture it, and never underestimate the power of listening to your body's whispers.
Read FAQs
A. To ease worries, focus on healthy habits, regular screenings, and open communication with healthcare providers. Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness to manage anxiety.
A. There isn't a single "biggest" symptom as it varies by cancer type. However, persistent unexplained symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, or unusual changes in bodily functions should prompt medical evaluation.
A. Cancer often begins with genetic mutations that cause cells to grow uncontrollably. These mutations can result from various factors like genetics, lifestyle choices, or environmental exposures. Early detection and intervention are crucial for effective treatment.